CSS: Introduction in CSS
The HTML markup language course covered various elements that have a default style - indented paragraphs, color-coded links, different-sized headings, etc. As a developer, you can change this styles or add entirely new ones. Want to add a background to the text? Resize elements? Create an animation? You can do all this with CSS (Cascading Style Sheets), the language that defines how HTML elements will look in the browser.
This CSS course is a logical continuation of the [HTML course] (https://code-basics.com/languages/html). Many of the tags and concepts that we'll be encountering along the way have already been covered.
The example below shows how to render text without using your CSS (i.e., using the styles your browser "puts in") and how to style a document using CSS.
Example of text with a standard layout
<p class="h2">Paragraphs</p>
<p>Paragraphs are created using a paired <code><p></code> tag with a small amount of text in the body. For example:</p>
<pre><code><p>First paragraph</p>
<p>Second paragraph</p></code></pre>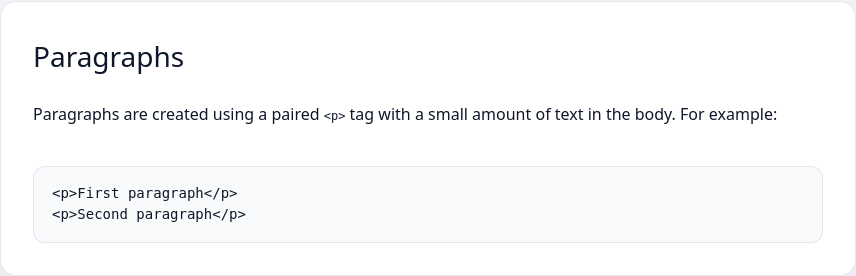
Example text with custom design
<p class="border-bottom display-6 pb-2">Paragraphs</p>
<p class="lead">Paragraphs are created using a paired <code><p></code> tag with a small amount of text in the body. For example:</p>
<pre class="bg-light my-4" style="border-left: 5px solid #673ab7!important;"><code><p>First paragraph</p>
<p>Second paragraph</p></code></pre>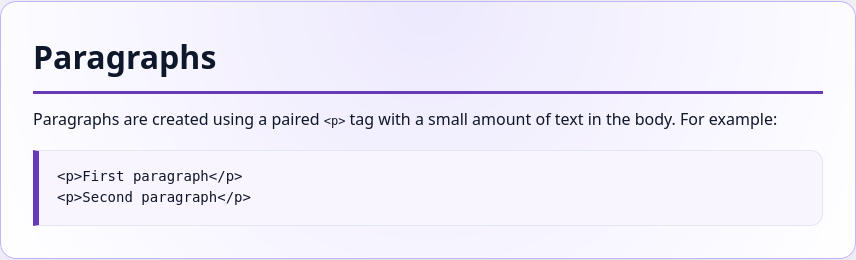
The text is now easier to read, and you can quickly separate code samples from descriptions. This course will cover the basic rules of CSS for working with text and blocks, which will allow you to design your text and visually structure information.
Instructions
Copy the code into the editor. Try substituting different values to see how the editor works. Tests expect a full copy of the code below.
<p style="font-size: 25px;">The first style change with CSS</p>If you've reached a deadlock it's time to ask your question in the «Discussions». How ask a question correctly:
- Be sure to attach the test output, without it it's almost impossible to figure out what went wrong, even if you show your code. It's complicated for developers to execute code in their heads, but having a mistake before their eyes most probably will be helpful.
Tests are designed so that they test the solution in different ways and against different data. Often the solution works with one kind of input data but doesn't work with others. Check the «Tests» tab to figure this out, you can find hints at the error output.
It's fine. 🙆 One task in programming can be solved in many different ways. If your code passed all tests, it complies with the task conditions.
In some rare cases, the solution may be adjusted to the tests, but this can be seen immediately.
It's hard to make educational materials that will suit everyone. We do our best but there is always something to improve. If you see a material that is not clear to you, describe the problem in “Discussions”. It will be great if you'll write unclear points in the question form. Usually, we need a few days for corrections.
By the way, you can participate in courses improvement. There is a link below to the lessons course code which you can edit right in your browser.
Your exercise will be checked with these tests:
const { test } = require('tests');
test(({ query, expect }) => {
const element = query(document, 'p');
const style = getComputedStyle(element);
expect(style).to.have.property('font-size', '25px');
});Teacher's solution will be available in:
20:00
